- Abstractionism
- Avant-garde
- Empire Style
- Animal art
- Baroque
- Genre Art
- Vanitas Art
- Renaissance Art
- Hyperrealism, Photorealism, Super Realism
- Landscape Style Art
- Gothic Art
- Graphics
- Impressionism
- Ippic Genre
- Historical Genre
- Classicism
- Cubism
- Mannerism
- Minimalism
- Modernism
- Modern
- Seascape (marine)
- Naturalism
- Still life
- Neoclassicism
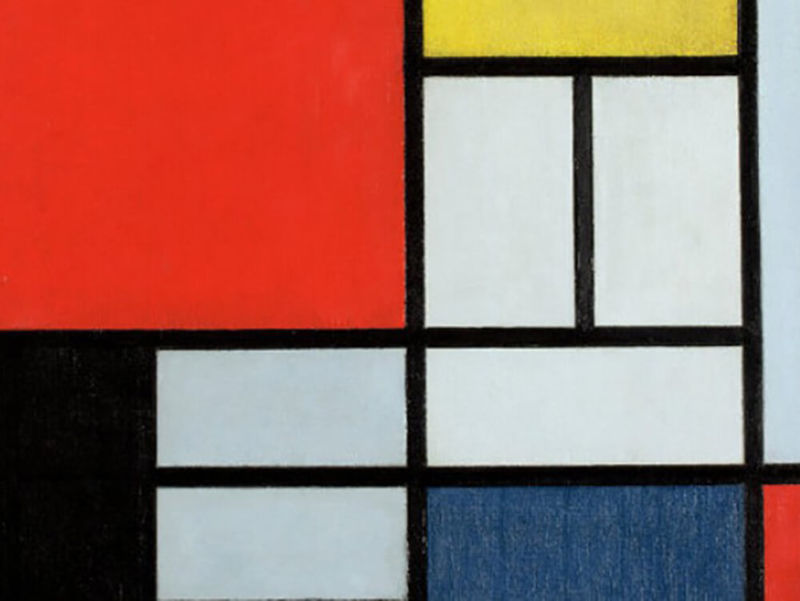
- Neoplasticism
- Nude
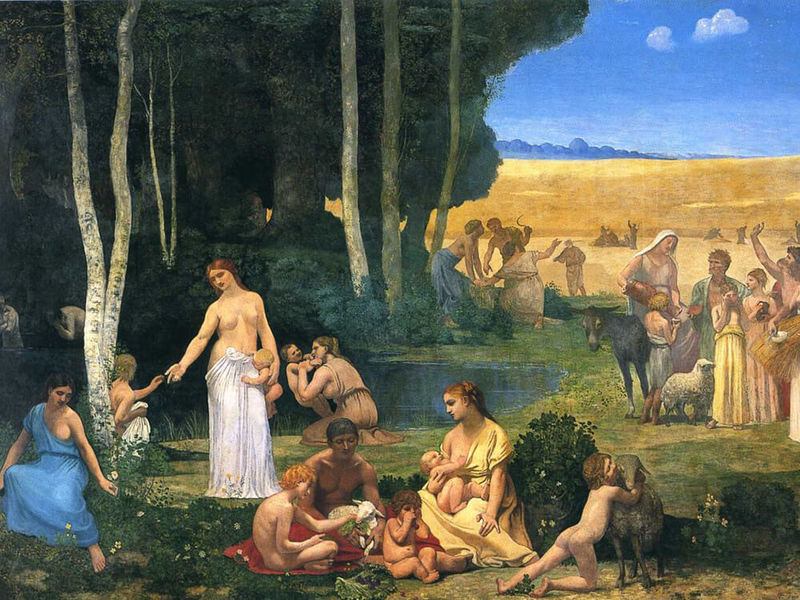
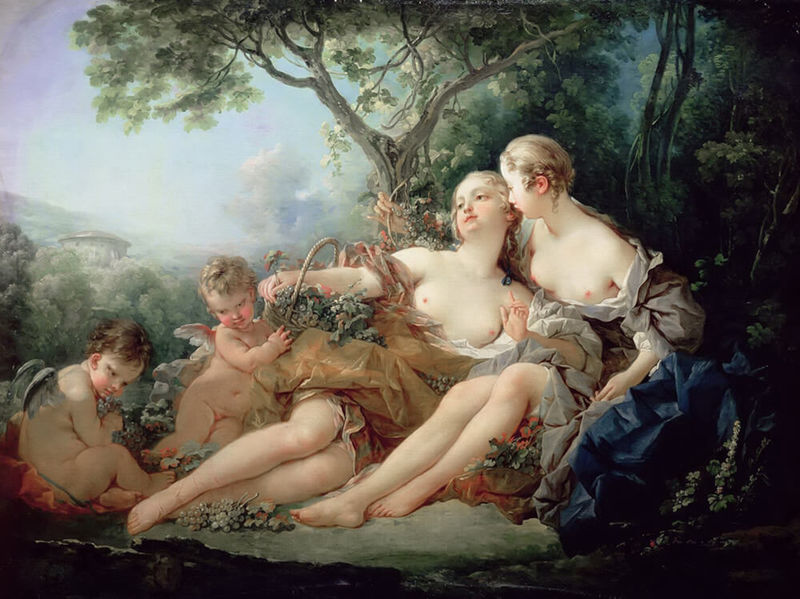
- Pastoral
- Pop art
- Post-Impressionism
- Postmodernism
- Primitivism
- Realism
- Rococo
- Romanticism
- Symbolism
- Street art
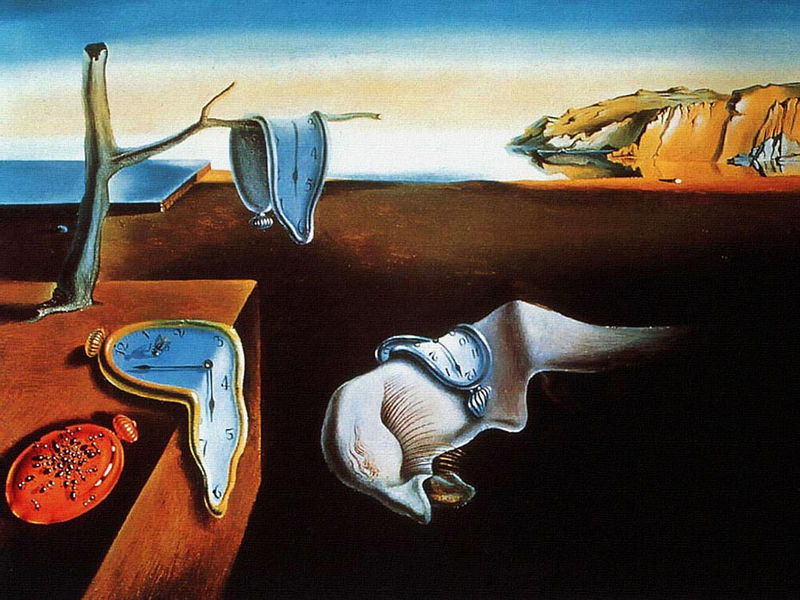
- Surrealism
There are many artistic techniques and techniques in the world that are constantly blending, changing and interacting. However, it is possible to highlight the main directions - and this is what our article is about. All styles of painting are presented here: the list includes not only the most famous varieties, but also their extraordinary variations.
Abstractionism
The name of this direction, which appeared in the beginning of the XX century, came from the Latin word «abstractio» - «distraction». The artists working in this technique abandoned realistic means of painting, trying to show the harmony and regularity of the world through geometric forms and color combinations. Abstractionism was a reaction to the realistic impulses of the time, aimed at expressing the inner world of the artist and abandoning the image of objects of reality. The goal of the masters was to reflect the organization of society and the environment, social processes. The most famous representatives are V. Kandinsky, K. Malevich, Pablo Picasso, Pete Modrian. Ukraine has also had its outstanding representatives of abstractionism, in particular, artists Mikhail Boychuk, Alexander Archipenko and Ivan Kavaleridze.
Ukrainian artists continue to actively develop abstractionism, creating amazing works that affect the world art scene.
Avant-garde
This style, whose name comes from f. words «avant» - «forward» and «garde» - «protection», developed in 1910-1940. It can be described as contradictory, complex, ambiguous and in need of reflection. The influence of avant-gardism can be traced to abstract expressionism, dadaism, constructivism, cubism, primitivism, suprematism, etc. who tried to find new ways and forms of image, to convey to the viewer their vision of the world. Avant-garde artists often expressed political, social, and philosophical views through their works, reflecting the complexity of the modern world.
Empire Style
This «imperial» or «royal» style (with Franz. «style Empire»), appeared in the first decades of the XIX century. During the reign of Napoleon I. He is distinguished by the paradox, pomposity, theatricality. The works are symmetrical and balanced, but supplemented by a variety of decorative elements - sculptures, draperies, military emblems. In Empire art, motives of military symbols, war trophies, warriors and military laureates are often encountered. Artists working in such a manner (of which Jacques-Louis David is best known) used antique subjects, ancient Egyptian, Etruscan and Pompeian ornaments, Renaissance painting techniques.
Animal art
The direction devoted to the depiction of animals and birds is the oldest in world art. Even in the Paleolithic Age (14,000 B.C. ) cave people painted on the walls of mammoths, horses, saber-toothed tigers. Later such motifs are found in the works of the Egyptians, Assyrians, Chinese, ancient Greeks and Romans. In different cultures, the animalist genre may have different symbolic meanings, reflecting spirituality, power, or rituals. Animalistic works can convey different aspects of the animal world, including their beauty, strength, tenderness, characteristics and behavior. And in XVII-XVIII centuries. This genre became popular in Flanders - dynamic and naturalistic pictures of animals created by Paolo Porporporo, Charles Jacques and France Snyders. In modern art, the animalist genre remains popular, allowing artists to express their ideas, observations and emotions through animal images.
Baroque
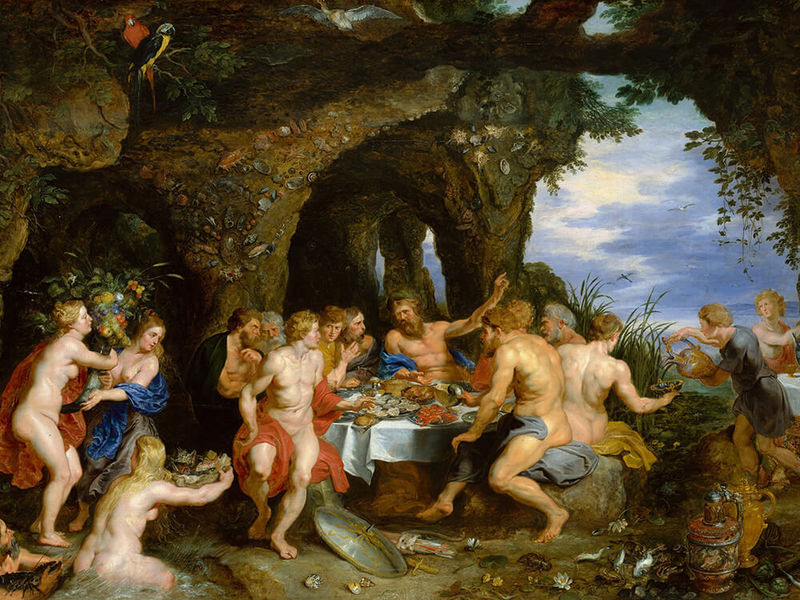
This style is a business card of Italy XVII-XVIII centuries. Some historians infer the origin of the name from Italy. «Barocco» is «strange», while others tend to believe that it is borrowed from the Portuguese language, where the words «perola barroca» means «pearl with defect». The main signs are contrast, tension, dynamism, greatness and grandeur. The Baroque combines illusion and reality, spiritual and material, sublime and funny. Baroque painting used bright and rich colors, emphasizing the decorativeness and dramatism of the compositions. The characteristic element of baroque painting was the use of movement and dynamic poses, which gave the paintings energy and emotional tension. His followers - Rubens, Caravaggio, El Greco, Velázquez - wrote mythological and biblical scenes, fantastic landscapes, parade portraits.
Genre Art
Drawings of everyday life were created in ancient Egypt and Greece. Similar scenes are present in European medieval manuscripts, bas-reliefs of churches and palaces. But as a separate style this direction was highlighted only in the XV-XIV century. When Jan van Eyck, Jan Vermeer, Antoine Watteau, and François Boucher joined the company. Artists capture workers and farmers, humorous episodes. In the 19th century. Painters began to depict the lives of the destitute, slaves and the sick, and in the 20th century. the paintings acquired ideological overtones.
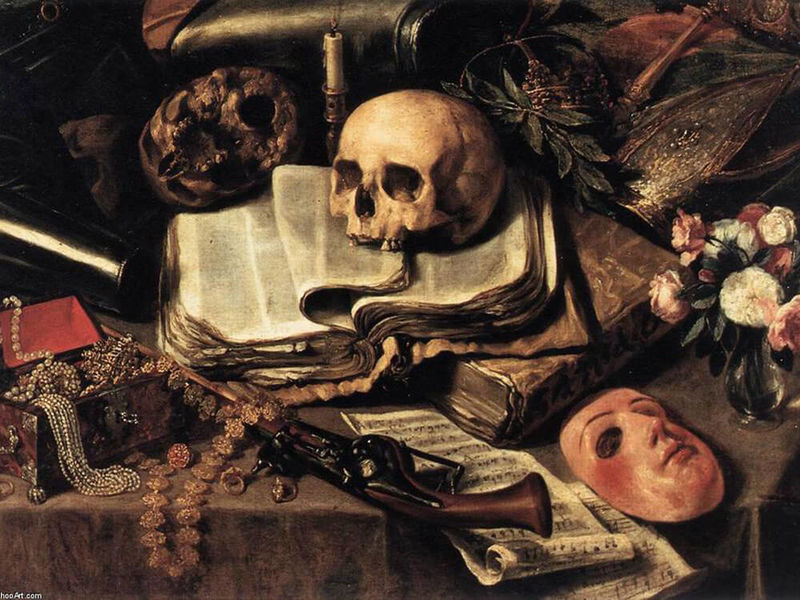
Vanitas Art
This direction began in the Baroque era. Its name «Vanitas» translates from Latin as «vanity, vanity» and goes back to the biblical verse: «Vanity, said Ecclesiastes, vanity, all vanity!». These are allegorical still lifes on which there is a human skull and other similar attributes - rotten fruit, fading flowers, soap bubbles, extinguishing candles or broken utensils. They are called to recall the futility and fleeting life, the inevitability of death. Vanitas became an important genre of art under the influence of the Catholic Counter-Reformation, which marked a diversion from secular worship and a return to religiosity. Vanitas compositions were complex, with carefully selected interacting objects, forming a symbolic message. Such works were created by Jacob de Gein, Simon Renard de Saint-André, Yurian van Streak.
Renaissance Art
This epoch (14th-16th centuries) became the cultural flowering of European history. The masters began to work with secular subjects, using humanistic ideals and antiquity as a perfect example of the world order. Traditional religious plots are filled with worldly content, realistic works (they are written with the laws of anatomy and linear perspective), paintings appear in plastic volume, and in the background are depicted landscapes or interiors. The revival was also a period of development of landscape painting, where nature became a separate object of study and aesthetic satisfaction. Famous Renaissance masters - Sandro Botticelli, Leonardo da Vinci, Rafael Santi, Michelangelo Buonarotti, Titian.
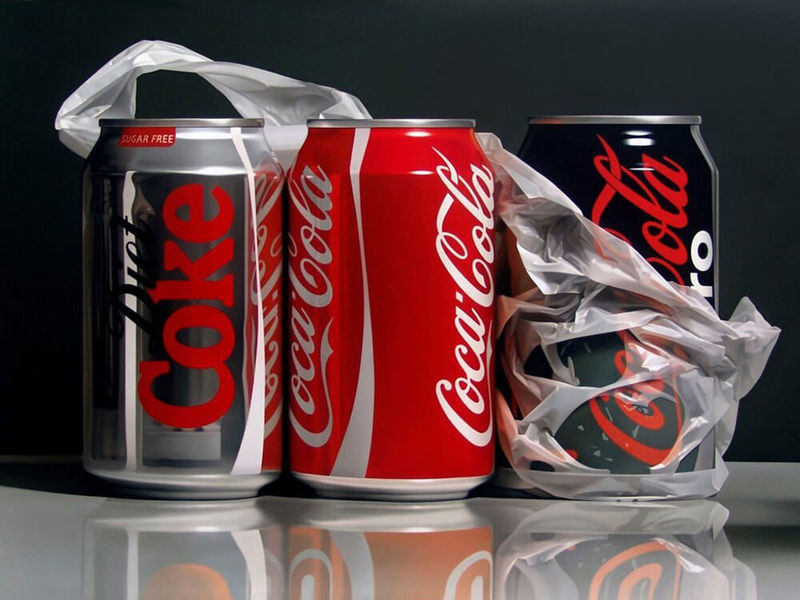
Hyperrealism, Photorealism, Super Realism
Such genre (from Ancient Greek. "Ὑπερ" that means "beyond" and lat. «realis" - "material, material") has arisen in the second half of XX century. and develops into the 21st century. The painting resembles high-resolution photography - all objects and scenes are detailed for the sake of creating the illusion of reality. But the image on the canvas could happen in life - this direction is different from surrealism. Artists working in these styles spend a lot of time studying details and working on the perfection of their paintings. Representatives of hyperrealism are Gerhard Richter, Klafek and Delcol.
Landscape Style Art
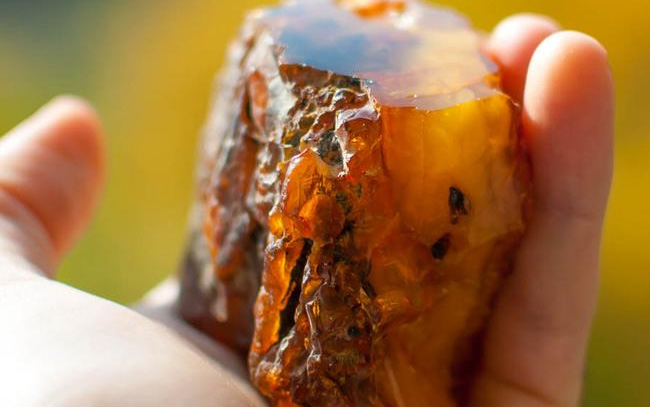
It's one of the most diverse styles. However, images of urban landscapes, streets, houses, and architectural objects are becoming increasingly popular. Creating such pictures, the master tries to reproduce not only the pictorial look, but also the emotions, emotions, feelings arising from his contemplation, to give the work expressiveness and spirituality. For example, these are works by F. J. Alekseev, Hendrik Averkamp, Gerrit Berkheide, as well as amber panels presented in our online store.
Gothic Art
This direction was discovered in the XII-XVI century in Europe. One of the main genres has become stained glass - from multicolored glass plates craftsmen created surprisingly complex and colorful images not only on theological, but also on everyday subjects. The art of book miniatures - illustrated manuscripts, watchbooks, psalms and the Bible - was flourished by the brothers Limburg and Robin Testar - and portrait painting. The artists moved away from the Byzantine canons, bringing individual traits, dynamics and emotions to the image. The Gothic style was highly emotional and expressive, emphasizing the religious and spiritual aspects of art. One of the most famous gothic artists was Jan van Eyck, whose style is known for its realistic details and insight of the images.
Graphics
The name of this art form comes from Dr. Grech. "γρᾰφικός" means the "written" and means the visual aids used by the master - lines, strokes, dots and spots. Unlike painting, color plays a secondary role. There are different types of graphics - machine tool, book, application, computer, industrial. One of the most famous types of graphics is lithography, where the image is created on a specially prepared stone or metal plate and is applied to paper or other material.
Graphic techniques allow artists to create detailed drawings, hatching, tone transitions and other effects that give the image expressiveness and reproduce different textures. The most famous masters working in this technique are Albrecht Dürer, Hokusai, Gustave Dore, Alphonse Muha and Alan Lee.
Impressionism
This style originated in the 19th century. in France. His representatives - Eduard Manet, Claude Monet, Edgar Degas, Alfred Sisley, Cézanne - wrote small and contrasting strokes, applying them according to theories of color. Thanks to this, the craftsmen were able to create works without mixing paints on the palette (this allowed them to work outdoors - another feature of Impressionism), as well as to abandon the black color. The artists tried to capture a fleeting impression of nature (hence the name of style), to convey the relativity of perception. Impressionist artists often worked in nature, recording the speed of light and atmospheric conditions in their paintings. Impressionism is still one of the most popular and outstanding styles in the history of art.
Ippic Genre
The name of this direction comes from the Greek word «hippos» - «horse». Such pictures you can see in the catalog of our online store - depicted strong, free horses, running through the expanses of plains or quietly grazing on green fields. Many paintings in this style have large formats to give more weight and impression of scale. Heroic figures with expressive gestures that emphasize their strength and courage are often depicted in the genre. The ippic genre had a great influence on the cultural consciousness and development of art, becoming one of the popular destinations in painting.
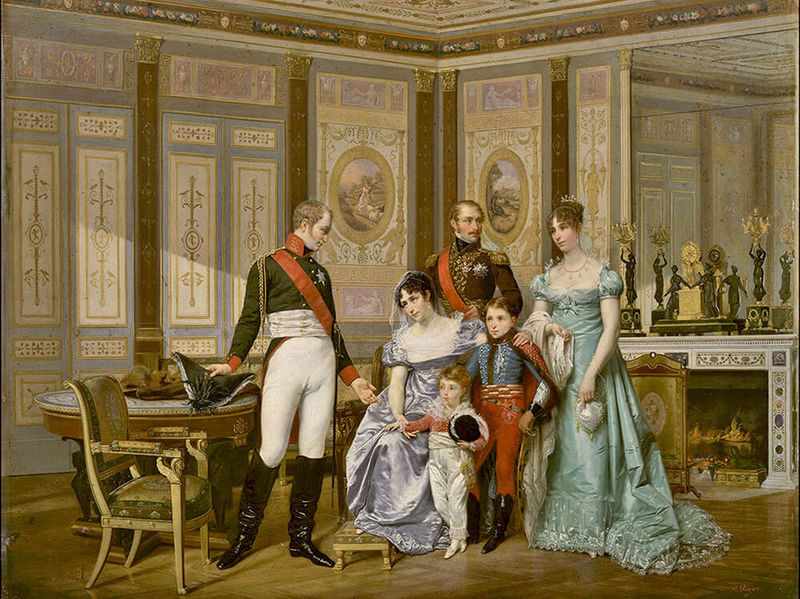
Historical Genre
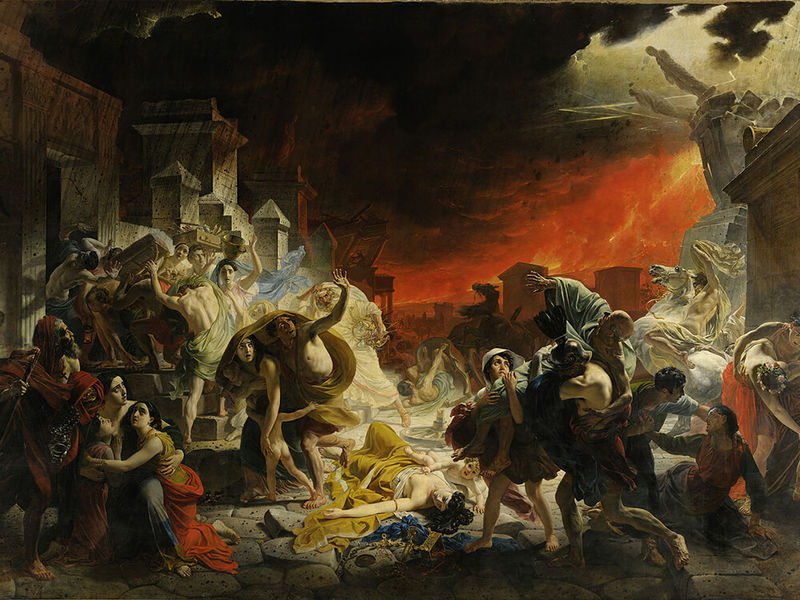
This style was formed during the Renaissance. Artists wrote important events of the past, and also captured stories of legends, the Gospel and the Old Testament. At the same time, their goal was often not the authentic depiction of incidents, but their glorification, the creation of an ideological myth. An example of such work is the work of K. Brullov «Pompeii’s last day». Artists of the historical genre can use symbolism, allegory, and other artistic means to emphasize certain ideas or meanings.
Classicism
The philosophy of Descartes (17th-19th century) is the basis of this direction. According to them, the work should triumph over chaos, reflecting important features of the manifested phenomenon and performing a socio-educational function. The aesthetic model became the work of the ancient era. Therefore, classical artists (Karl Brullov, Antonio Canaletto, Nicola Poussin) often turned to mythological subjects. The main elements were the line and the light - they helped to reveal plastic shapes and objects, to separate spatial planes. This style left a marked mark in the history of art, helped to revive the interest in antique culture and created the basis for further development in art.
Cubism
The origin of this genre is very unusual - it is believed that the impetus for its emergence was a letter by Paul Cézanne to Pablo Picasso, in which he advises the young painter to consider nature as a combination of simple geometric forms. Therefore, the Cubist masters, working in the beginning of the XX century. represented reality as a set of conventional stereometric objects and planes. Thus, in such a technique some paintings of Picasso («Avignon Maidens», «Accordionist»), paintings of Juan Gris, Marcel Duchamp, S. I. Schukin.
Mannerism
This Western European style developed in the 16th and 17th centuries. Its distinguishing features are the chanting of the spirit, often combined with the accented eroticism, the roughness of lines, the deformation of figures, the tension of poses. Such paintings often have an overloaded composition and a rich palette. This style often used perverse proportions, elongated figures, and unexpected color combinations. This style caused much controversy and debate, as it contradicted the classical canons and requirements. Representatives of this genre are Arcimboldo, Francesco Parmigianino, Jacopo Pontormo.
Minimalism
The movement was founded in the United States in the late 1960s. It is characterized by extreme simplicity, literality, image asymmetry, simplicity and monochrome. However, such paintings are filled with metaphors and associations, a hidden meaning. Minimalist artists (Carl Andre, Dan Flavin, R. Rayman) abandoned realism and subjectivity, allowing viewers to perceive the painting themselves without the artist’s interpretation.
Modernism
This current (from the lats. «modernus» - «modern») became a turning point in the world of art. The masters stopped showing the world around them, turning to the author’s vision, feelings and experiences. Often this approach was accompanied by an epatage, a challenge, and the breaking of established canons. However, it is believed that it is this that allows to portray the true reality, the inner freedom, the aspiration for progress. These include Dadaism, Impressionism, Cubism, Surrealism, Futurism, Expressionism, etc.
Modern
Under this name, a variety of styles of painting, from Art Nouveau to secession and art nouveau, were hidden in the 19th and early 20th centuries. The works of artists working in this genre were often used as elements of the interior, so they are characterized by decorativeness, conventionality, asymmetry, a combination of large planes and subtle nuances, ornamental backgrounds, on which persons and figures stand out. In this genre created Gustav Klimt and Mikhail Vrubel.
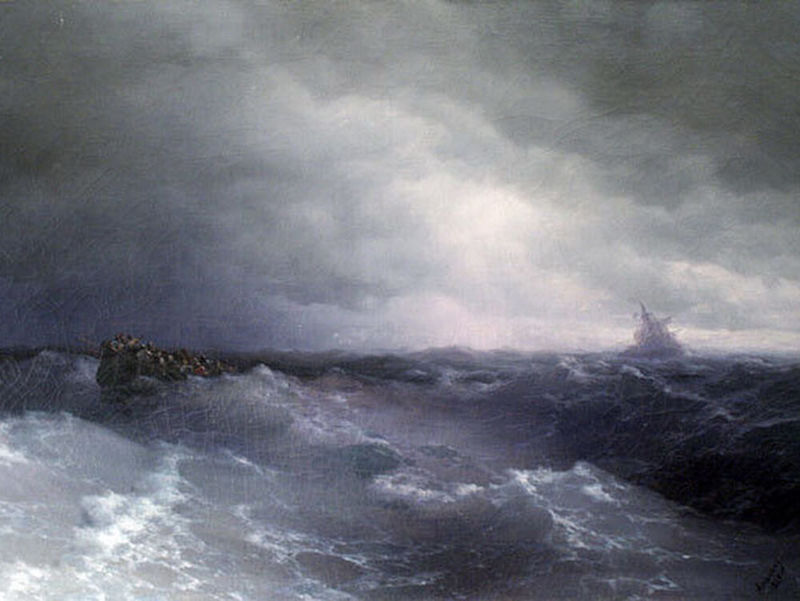
Seascape (marine)
This genre (from Lats. «marinus» - «marine») stood out as an independent in the XVII century. in the Netherlands. It shows views of vast expanses of ocean, scenes of battles between ships, storms, sunsets over the sea. Marine landscape artists use a wide color palette to convey the mood and emotions associated with the sea. Marine landscapes can be calm and melancholic, or expressive and energetic, depending on the artist’s intention. Bright representatives - William Turner, J. K. Aivazovsky.
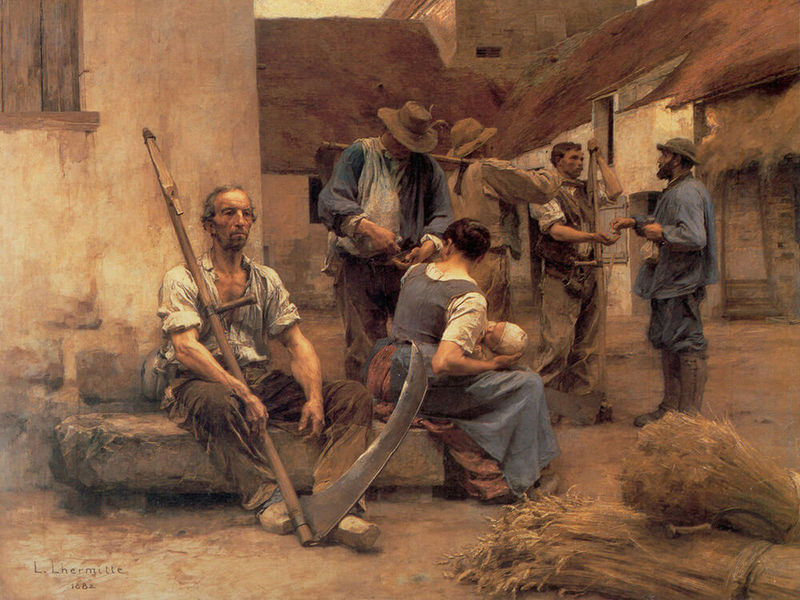
Naturalism
This phase of realistic painting began and developed in the 1870s. The painters-naturalists (D. R. Knight, A. Mutt, L. Lermit) sought to capture their contemporary reality, the daily lives of peasants and workers without any circumstance, impartially and objectively. Therefore, they often wrote scenes of violence and brutality, interpreting them as a Darwinian struggle for existence.
Still life
These paintings depict inanimate objects - flowers, fruits, game, served tables, kitchen utensils, household items. Sometimes each object is given a symbolic value, but in most cases they demonstrate the well-being of the owners, serve to decorate the interior. The most famous representatives of this genre are the Dutch Jacob de Gein, Clara Peters, Peter Klas, Jan Davids de Hem.
Neoclassicism
This aesthetic direction was established in the late 18th - early 19th century. The subjects of the painters turn to antiquity, and all the characters are attributed to the grandeur, rigour, and monumentality typical for this epoch. Strict axial symmetry prevails, no decorative elements. The most famous artists of the genre - Lawrence Alma-Tadema, Anton Rafael Menge, Feuerbach Anselm.
Neoplasticism
This current of abstract art existed in 1917-1928. in Holland. Its creator is Pete Mondrian, who brought together artists from the magazine «DeStijl». It was he who first began to depict on his paintings «pure plastic» - large rectangular planes painted in bright colors. Such ideas influenced the architecture, design and printing business of the 20th century.
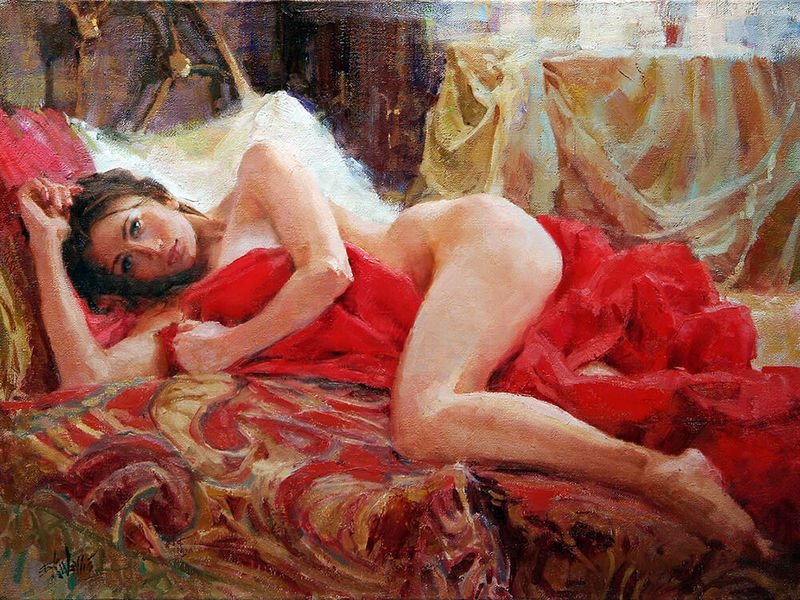
Nude
This genre (from Fr. «nudité» - «nakedness, innocence») is designed to show the beauty of the naked human body. It first appears in the Stone Age, blossoms in the Age of Antiquity, and is experiencing a new surge in the works of the Renaissance, Baroque and Modern times. Such works demonstrate sensual, full-fledged perception of the world, ideal ideas about beauty. In this technique painted paintings of Titian, Rubens, François Boucher.
Pastoral
This style, popular in Italy in the early XVI century. poeticizes peaceful, simple rural life (hence its name - from French «pastorale» translated as «shepherd»). The artists who worked in this manner (Giordon, Anntuan Watteau.NikkoloKannichi) wrote happy and harmonious life in the midst of nature, funny scenes with nymphs, fauns, courtesans and peasants.
Pop art
This is commonly referred to as the current of popular or natural art that emerged in Western Europe and the United States in the 1950s and 1960s. Its representatives (Andy Warhol, Jasper Jones, Roy Lichtenstein) show to the audience objects of mass culture, household items, packaging of goods and even fragments of various mechanisms placed in a different context. It is believed that this allows you to reconcile with the world of platitudes and vulgarity, to challenge everyday life, to see the beauty in the daily routine.
Post-Impressionism
This term refers to a set of artistic trends that appeared in the second half of the 19th - early 20th century. They are characterized by the desire to depict the basic, natural features of reality, philosophical and symbolic objects, long states of life, sometimes with the use of decorative styling. The greatest masters of this current - Vincent van Gogh, Paul Gauguin, Henri Toulouse-Lautrec.
Postmodernism
This genre emerged as a way of opposing modernism, and Umberto Eco defined it as a mechanism to help change one cultural discourse to another. In this style there are no universal canons - the only goal are freedom of the creator and the absence of restrictions. It is characterized by narrative, harmony of forms, borrowing from different eras and styles. Principal representatives are Jackson Pollock, Mark Rothko, Ellen Frankenthaler, Arnett Newman.
Primitivism
This genre, born in the XIX century. provides a deliberate simplification of the picture, making it similar to children’s drawings or cave paintings. Marc Chagall, Nico Pirosmani, Grandma Moses, Henri Rousseau, did the same.
Realism
While previous painting styles with examples of paintings had fairly clear features and criteria, realism is more of an aesthetic position. According to her, the task of art is to record the world as accurately and objectively as possible. Various trends in this direction are represented by the works of Caravaggio, Jan Vermeer, Velázquez, the paintings of Edgar Degas and Edward Hopper, the works of Gustave Kurbe, Theodor Rousseau, I. I. Shishkin, I. Repin.
Rococo
This current (its name comes from fr. «rocaille» - «crushed stone, shell») appeared in France in the XVIII century. Characteristic features of style - grace, lightness, playfulness. It glorifies youth, beauty, and escape from reality. The compositions are full of decorative details, graceful patterned rhythm. François Boucher, Giambatista Tiepolo, Fragonard wrote in this spirit.
Romanticism
The paintings of the painters who worked in this manner sing emotions, inner impulses, fears, love and hatred. With the help of juicy colors and strong, confident brushstrokes, artists captured fantastic landscapes, beautiful girls, rioting elements and fairy tales. Representatives of this genre - I. Aivazovsky, Francisco Goya, Eugene Delacroix.
Symbolism
This current is one of the largest in the art of the XIX-XX centuries. The masters tried to depict the life of the soul - a vague, vague, full of experiences and subtle feelings, the mystery of being, its mystical and mysterious side. Mikhail Vrubel, Aubrey Birdsley, Gustav Moreau, Eugène Carriere performed in this manner.
Street art
Such art is not for exhibitions and galleries. It develops on the streets, in public places and is an integral part of the city landscape. This includes graffiti, stencils, nondimensional posters, sculptural installations. Its members often hide behind aliases and tags (personal stylized logos) - Julio 204, Taki 183, Space Invader.
Surrealism
Characteristic features of this current, which emerged in the 1920s. in France - allusions, paradoxical combinations of forms, deformation of reality. It is designed to elevate the viewer, to separate the spirit from the reality, to break the everyday conception of the world. The greatest surrealist masters are Salvador Dalí, Max Ernst, Rene Magritte.

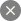














































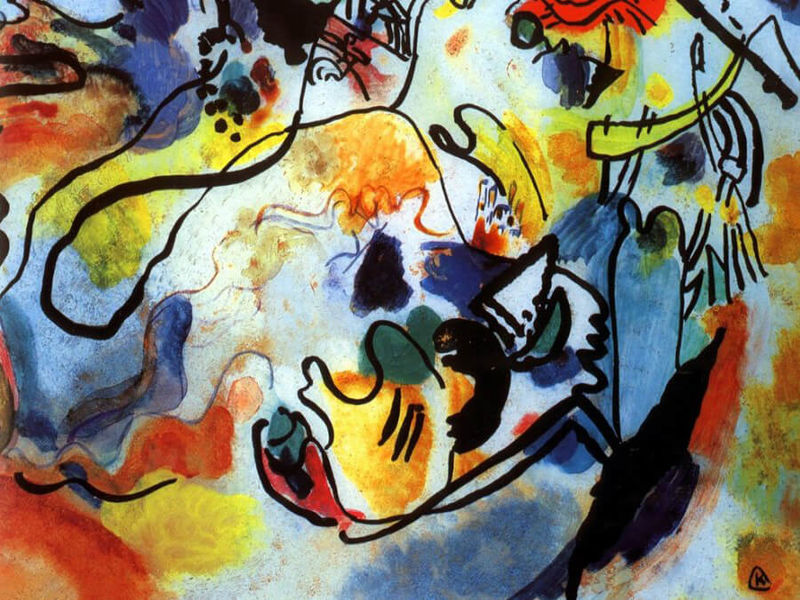
















.jpg)



.jpg)



















Спасибо за Ваш голос